Understanding Measurement Errors
Definition of Measurement Error
Measurement error refers to the difference between the observed value and the true value of a quantity being measured. It is an inherent part of the measurement process and can arise due to various sources, including human error, instrumental limitations, and environmental factors. These errors occur due to human factors such as observer bias, lack of training, and fatigue. Understanding measurement errors is crucial in various fields, including science, engineering, and research, as it can significantly impact the accuracy and reliability of results.
Importance of Measurement Errors
Measurement errors can have a significant impact on the outcome of experiments, research studies, and decision-making processes, affecting data accuracy. Inaccurate measurements can lead to incorrect conclusions, flawed designs, and ineffective solutions. Therefore, it is essential to identify and minimize measurement errors to ensure the validity and reliability of results. By understanding the sources and types of measurement errors, researchers and scientists can take steps to mitigate their effects and improve the accuracy of their measurements.
Types of Measurement Errors
Measurement errors can be broadly classified into two categories: systematic errors and random errors. Understanding these types of measurement errors is crucial in research and experimentation to ensure accurate and reliable results. Systematic errors are consistent and predictable, while random errors are unpredictable and vary in magnitude and direction.
Systematic Errors
Systematic errors are consistent or proportional differences between the observed and true values of a measurement. These errors can be caused by various factors, including instrument calibration, environmental conditions, and human bias. Systematic errors can be further divided into three subcategories:
Instrument-related errors: These errors occur due to faulty or poorly calibrated instruments, which can lead to inaccurate measurements. For example, a scale that is not properly zeroed will consistently give incorrect weight readings.
Environmental errors: These errors occur due to external factors such as temperature, humidity, and lighting, which can affect the measurement process. For instance, a thermometer might give incorrect readings if the ambient temperature fluctuates.
Human errors: These errors occur due to human factors such as observer bias, lack of training, and fatigue. An example is a researcher consistently reading a measurement incorrectly due to poor eyesight or misunderstanding the instrument’s display.
Systematic errors can be reduced by using calibrated instruments, controlling environmental conditions, and training observers to minimize human bias. By addressing these factors, researchers can significantly improve the accuracy of their measurements.
Random Errors
Random errors are chance differences between the observed and true values of a measurement. These errors are unpredictable and can occur due to various factors, including instrument noise, sampling errors, and human variability. Unlike systematic errors, random errors do not have a consistent pattern and can vary in magnitude and direction.
Instrument noise: This refers to the random fluctuations in the readings of an instrument, which can lead to variability in measurements. For example, electronic noise in a digital thermometer can cause slight variations in temperature readings.
Sampling errors: These occur when the sample being measured is not representative of the entire population, leading to random variations in the data. For instance, measuring the height of a small group of people may not accurately reflect the average height of the entire population.
Human variability: This includes random differences in how different observers or the same observer at different times take measurements. For example, slight differences in how a researcher positions a measuring tape can lead to variations in recorded lengths.
Random errors can be reduced by increasing the sample size, using multiple measurements, and controlling extraneous variables. By taking these steps, researchers can minimize the impact of random errors and obtain more reliable results.
Two types of measurement error – bias and precision
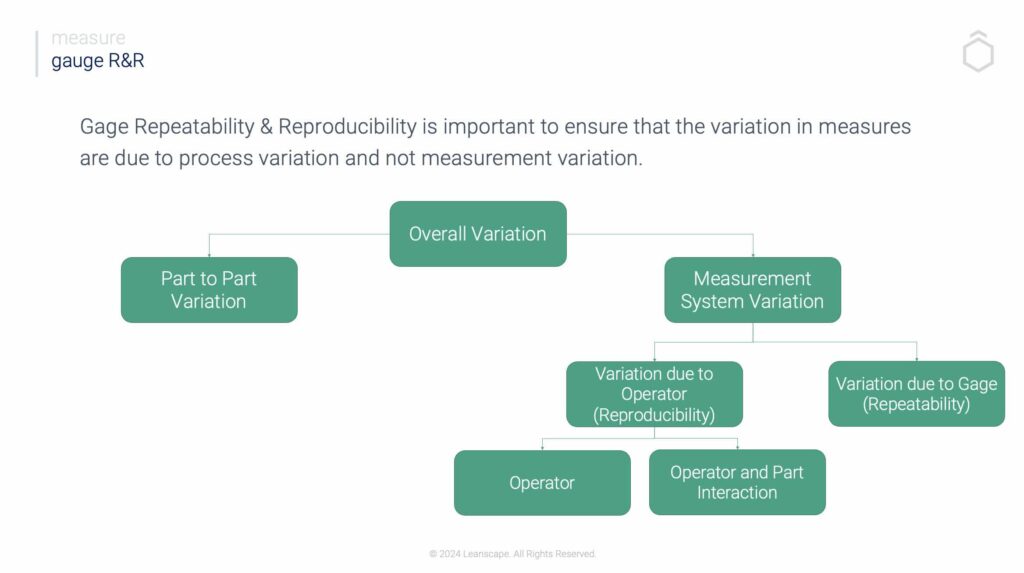
Different types of measurement errors can have an unnecessarily negative impact on data accuracy, leading to skewed results. Two common types of measurement errors are bias and precision errors and they can significantly affect data accuracy. Bias is a type of systematic error that causes inaccurate measurement, known as measurement bias, resulting in data points being consistently higher or lower than the true value. Systematic errors, in general, can significantly impact the accuracy of research findings and must be addressed to ensure valid conclusions. Precision, also known as random errors, occurs when individual measurements vary wildly from their mean. This can cause the spread of data points to be much larger or smaller than expected. It is important for surveyors and researchers to recognize these two common types of measurement errors in order to ensure accurate data collection and reporting.
Precision errors can be further divided into two categories: repeatability and reproducibility.
Repeatability errors, one of the types of errors, occur when the same measurement is repeated multiple times, resulting in different data points each time. Reproducibility errors, another type of error, occur when independent measurements are taken of the same material or process being examined, leading to inconsistent results. Precision, also known as random errors, occurs when individual measurements vary wildly from their mean, highlighting issues with measurement precision. Both of these types of precision errors can lead to inaccurate reporting and should be addressed during projects when collecting data.
Sources of Error in Measurement
Measurement errors can occur due to various sources, including instrument-related errors, environmental errors, and human errors. Understanding these sources of error is essential for minimizing their impact and ensuring accurate and reliable research results.
Instrument-Related Errors
Instrument-related errors occur due to faulty or poorly calibrated instruments, which can lead to inaccurate measurements. These errors can be caused by various factors, including:
Instrument calibration: Instruments that are not properly calibrated can lead to systematic errors. For example, a miscalibrated scale will consistently give incorrect weight readings.
Instrument sensitivity: Instruments that are not sensitive enough can lead to random errors. For instance, a thermometer with low sensitivity may not detect small temperature changes accurately.
Instrument noise: Instruments that produce noise can lead to random errors. Electronic noise in a digital device can cause fluctuations in readings, affecting the accuracy of measurements.
Instrument-related errors can be reduced by using calibrated instruments, regular maintenance, and proper training on instrument use. Ensuring that instruments are in good working condition and used correctly is crucial for obtaining accurate measurements.
In research, errors in measurement can have a significant impact on the accuracy and reliability of results. Understanding the types of measurement errors and sources of error is crucial in minimizing errors and ensuring accurate results. By using calibrated instruments, controlling environmental conditions, and training observers, researchers can reduce systematic errors and random errors, leading to more accurate and reliable results.
Calculating Measurement Errors
Absolute Error
Absolute error is a measure of the difference between the observed value and the true value of a quantity. It is calculated using the formula:
Absolute Error = |Observed Value – True Value|
For example, if the observed value of a quantity is 10.2 units and the true value is 10.5 units, the absolute error would be:
Absolute Error = |10.2 – 10.5| = 0.3 units
Absolute error is an important measure of measurement error, as it provides a quantitative estimate of the difference between the observed and true values. By calculating the absolute error, researchers and scientists can evaluate the accuracy of their measurements and identify potential sources of error. Relative error, on the other hand, compares the absolute error to the true value, providing a measure of the error in relation to the size of the true value.
100% Free Fundamentals of Lean COURSE
How to avoid or reduce measurement error in your projects
To avoid or reduce measurement error in your research study, it is important to select reliable, valid instruments that measure the variables of interest and ensure proper calibration. Errors in measurements can also arise due to external conditions such as temperature, pressure, and humidity, which should be controlled as much as possible. Moreover, you should use standard scoring methods for collected data and provide clear directions for participants when completing assessment tasks. For example, if your research study requires self-reports from participants related to their feelings and thoughts about a certain topic, ensure that participants understand what information must be reported before beginning. Finally, using multiple measures and collecting data regarding the same concept from different sources can help verify and confirm the accuracy of the results.
The importance of taking measures to reduce measurement error
Taking the right steps to reduce measurement error and ensure measurement reliability is crucial in research and many other areas. Whether you’re conducting scientific research, gathering data on sales figures or analysing customer opinion, obtaining accurate measurements can make all the difference. From getting reliable results to informing decision making, reducing measurement error leads to more effective outcomes. Knowing what sources of errors exist and taking precautions are key for successful data collection and analysis. This means using robust and reliable methods as well as double-checking findings to ensure accuracy. Taking these extra measures when it comes to collecting meaningful data will help any organisation make sound and insightful decisions.
Examples of sources of bias and precision in measurements
In any scientific study, sources of a bias and precision in measurements must be taken into consideration to ensure the results are accurate. Examples of error include the observer effect, which can produce inaccurate results depending on how familiar a researcher is with their chosen subject, as well as selection bias and systematic bias, where samples are not selected randomly and therefore do not accurately reflect wider populations. Examples of precision in the measurement include double-blind trials which help to prevent bias by ensuring researchers and participants are kept unaware of each other’s identities, as well as random number generation, where software is used to help select unbiased random samples. To conclude, these types of sources both provide important considerations for researchers when conducting any kind of scientific study.




















